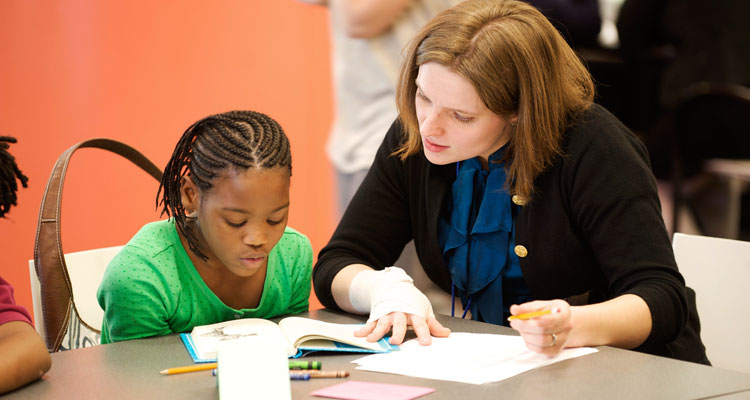
All students face challenges at school, but dyslexic students have greater difficulty than others. Their disability makes it a challenge to read. They transpose letters, have difficulty concentrating on reading, and may see words as blocks of color. How can you as an educator better understand, identify, and help these struggling students?
Understanding and Identifying Dyslexic Students
PBS.org points out that “research suggests that about 17 percent of the population has dyslexia.” (Review the common symptoms of learning disabilities to determine if your child may have dyslexia.) Because dyslexia is such a common disability, it is all the more vital for teachers and parents to have more than a vague idea of what dyslexia entails. The following resources can help.
- The Yale Center for Dyslexia & Creativity provides a wealth of information about dyslexia and how to identify it in students. The website has sections specifically geared toward parents, educators, and people with dyslexia.
- “What’s Going On Inside A Dyslexic Student’s Brain?” That question, posed on KQED’s MindShift blog, is well worth the attention of adults who want to help dyslexic students. A short video on the blog gives an overview of dyslexia.
- The International Dyslexia Association provides a comprehensive overview of dyslexia. This paper includes information on what dyslexia is and its signs and symptoms. There is also a list of additional resources for those who wish to dig deeper into the subject.
- Is dyslexia the same for every student? No. Dyslexia-reading-well.com gives an overview of the different types of dyslexia.
- Understandingdyslexia.co.uk provides a free digital copy of a booklet that explains dyslexia. The booklet uses relatable examples to highlight how dyslexia affects the people who have it, and it encourages parents to make necessary adjustments in their child’s education to help them fully absorb what they learn.
Teaching Dyslexic Students
Whether you are a professional educator or a parent who chooses to teach your children at home, helping dyslexic students presents a special challenge. The following resources will help you to meet that challenge.
- Internet4classrooms.com gives a list of resources that can help educators teach dyslexic students in the classroom. The resources include information as well as printable activities and worksheets.
- An article on dyslexia.com gives practical tips that teachers can use to help students with dyslexia. There are different tips for teaching reading, math, and spelling.
- A paper entitled “Teacher Strategies for Dyslexics” gives facts and stats about dyslexia. Beginning on page eight, there are strategies for teaching students with the disability. These strategies include breaking information into small pieces, making sure that dyslexic students sit near the front of the classroom, and combining verbal and visual information delivery.
- Dyslexia Victoria Online contains information about dyslexia as well as strategies for teaching dyslexic students. The “Five Steps to Learning for Dyslexics” outlines the process that students go through as they assimilate information.
- Sheknows.com provides a list of seven ways that educators can help dyslexic students maintain a positive frame of mind. One of the strategies involves giving students examples of successful individuals who have dyslexia, like Orlando Bloom and Whoopi Goldberg.
Dyslexia makes learning more difficult, not impossible. The above resources can help you help dyslexic students thrive. K12 aims to help all kinds of students obtain a thorough and meaningful education. Request free information about K12’s programs and products to see if they may be able to contribute to your students’ success.
Image Credit – US Department of Education / CC by 2.0